What is IBC?
Following the definition from the project website: “IBC is an interoperability protocol for communicating arbitrary data between arbitrary state machines.” What does that mean? It means that IBC was designed to securely process transactions on two chains without need to involve a third party.
What are alternatives?
IBC is a pretty new protocol (designed in 2019), but the problem of establishing transactional communication between blockchain is very common and not new. So how did the world manage to solve interoperability between chains before IBC? The main way developers managed to overcome this problem was bridging the networks. It allowed the exchange of assets (like NFT or ERC-20 based tokens) between networks.
There are at least a few options that exists on the market and try to address this problem:
- Cross-chain bridges
- XCMP - Polkadot version of cross-chain communication
What problems can IBC solve?
More than 1.5M transactions on 25 blockchain networks are executed every month using Inter Blockchain Communication protocol. IBC is an open source interoperability protocol designed by Cosmos for exchanging digital assets (tokens, interchain accounts, oracle data) between chains without the need of third party solutions like dedicated bridges.
Compared to third party bridges, IBC brings several improvements in different areas:
- performance/speed of transactions
- no need of trust to third parties
- lower costs
Performance
One of the biggest problems IBC solves is the speed of transactions. IBC protocol is faster than a cross-chain bridge because it eliminates the need for a third-party intermediary in order to transfer data or assets between two different blockchains. Cross-chain bridges, on the other hand, rely on a third-party service that must process the data or assets before they are transferred to the other blockchain, which can create delays.
Security (lack of third party)
Protocol brings data exchange privacy to a higher level by ensuring that data is kept confidential and secured. They also make sure that only authorized parties can access the data.
To make it more juicy: lack of third parties (which usually is based on centralized solutions) means that there is no single point of failure, making this type of solution much harder for hackers to attack and exploit the system.
The architecture of IBC (transport layer & application layer) allows to take control over process building and sharing datagrams between parties. The application layer is responsible for providing security services like authentication, authorization and auditing of data. Additionally there is still a possibility to extend the security layer with custom solutions like encryption.
Lower costs
When considering high volumes of data transferred between chains, costs of transactions become a crucial aspect. IBC allows to decrease costs of transaction fees as the need to include additional networks into the process. These aspects of IBC create opportunities for creating high horizontal scaling dAps without the need to create complex off-chain and on-chain solutions.
How does IBC work?
The base of IBC protocol are light clients and relayers. During communication both parties (Chains) use light customers and relayers, one chain without having to use a trusted third party can reach a consensus state of another chain. Both sides do not send messages directly, once one chain changes his state by creating a data pocket permissionless off-ledger relayers process scanning this state and transferring data to the other chain. Relayers are off-chain processes responsible for executing data on opposite chains by using one or more channels of communication.
Relayers use light clients of chains for verifications of incoming messages. Light clients are algorithms responsible for tracking and verifying the consensus state of other blockchains against the client's consensus state. Examples of light clients are Tendermint or Solo Machine.
IBC is designed up to two layers - the transport layer (TAO) and the application layer. The transport layer implements infrastructure mechanisms for secure connections and data authentication. The application layer is responsible for the packaging and interpretation of data; all is opaque to the protocol. The architecture of IBC layers is similar to the bottom-up TCP/IP internet protocol. It enables cross-chain communication by defining a set of requirements and functions used by the protocol.
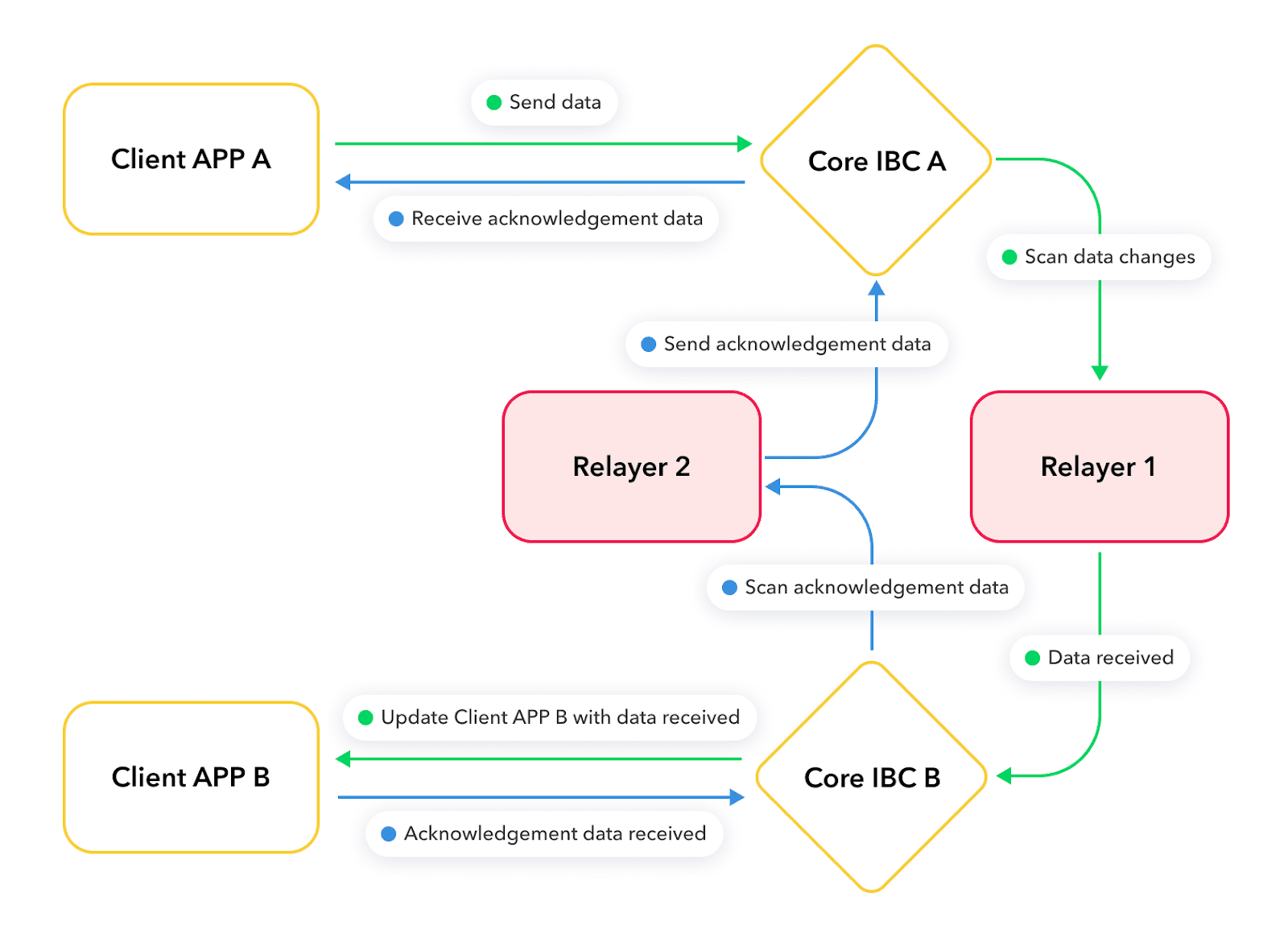
Let me explain the picture above based on a real example - let’s transfer 1 ETH from the Ethereum Mainnet to Cosmos. In this scenario our Mainnet is “Client APP A” and Cosmos is “Client APP B”:
- Client app A is locking asset A in the network
- Relayer 1 is scanning CoreIBC A network for changes in state - once detected it locks the asset read data and sends it to Core IBC B on a different network
- Core IBC B is sending data to Client APP B and the asset is minted on the second network
- After successful minting acknowledgement data is set and Relayer 2 is sending this data to CORE IBC A that informs about successful minting on second network
Assets minted in the second network can be sent back to the first network - it will execute unlocking of locked assets. Importantly IBC is not sending tokens itself - just sending value. On the second network a new instance of the token is minted based on value of the asset from the first network
Summary
IBC is a solution which is already extensively used by various DeFi projects. Cosmos and Osmosis is using IBC for critical financial and asset exchanges. Gravity DEX uses IBC to connect with multiple blockchains and execute trades across them. This is essential to ensure that users can trade assets from different blockchains and that their assets are safe and secure. Additionally, IBC allows the Gravity DEX platform to provide a secure and reliable trading experience, ensuring that trades are executed quickly and accurately. Many crypto wallets like Metamask and Keplr support IBC, making it easy to connect to a wallet and transfer tokens which is of great importance in the growth of adaptation of blockchain technology and the IBC itself. Will it beat the world? Well … the blockchain world is evolving really fast, so there is a huge chance that in the near future some new competitors will arise, but for now it’s one of the best options available on the market.


